AFO: see Ankle-Foot Orthosis
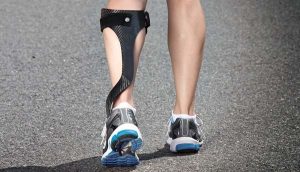
Ankle-Foot Orthosis (AFO): A walking aid used to improve gait by reducing or preventing movement of the lower limb by supporting weak muscles. An AFO may be used to help maintain joint alignment, accommodate deformity, and reduce spasticity. They are commonly used in MS for foot drop. You can buy an AFO on your own or have one custom-made.
Autoimmune Disease: A disease that occurs when a person’s immune system begins to mistakenly attack its own healthy, normal cells. MS is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the healthy cells of the central nervous system.
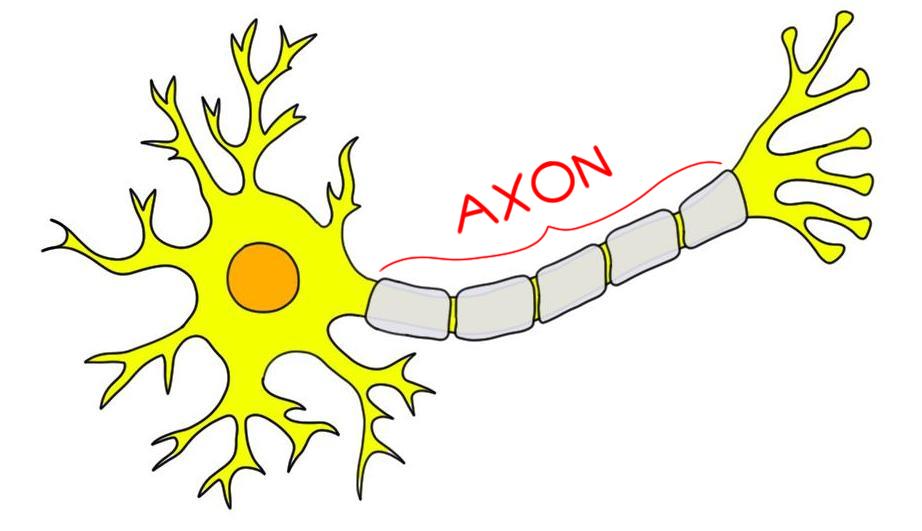
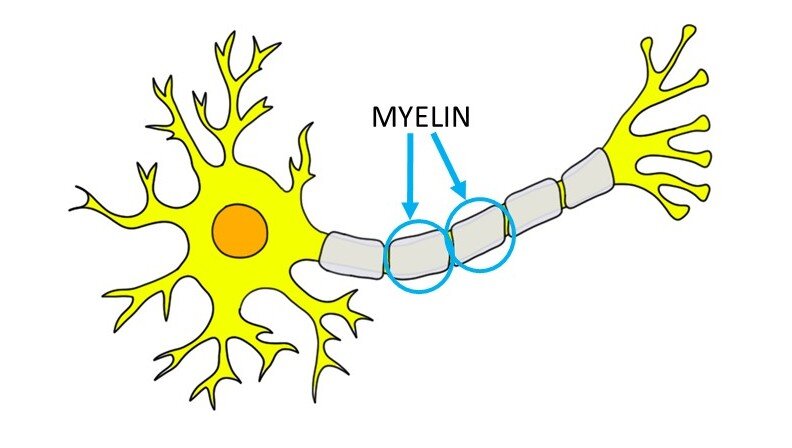
Axon: A nerve fiber. Axons extend from neurons (nerve cells) and transmit messages to the next neuron.
B-Cell: Also known as a B-lymphocyte, a B-cell is a type of white blood cell. B-cells produce antibodies that bind to foreign substances, such as viruses, and neutralize them. B-cells are thought to play a key role in MS by helping initiate the attack on the central nervous system.
Babinski Reflex: A normal reflex in infants, but may indicate a brain or nervous system disorder if it occurs in anyone older than two. The sole of the foot is firmly stroked causing the big toe to move upward and the other toes to fan out.
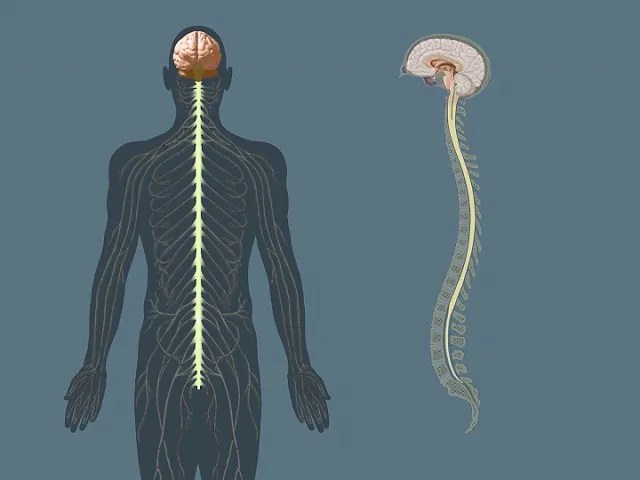
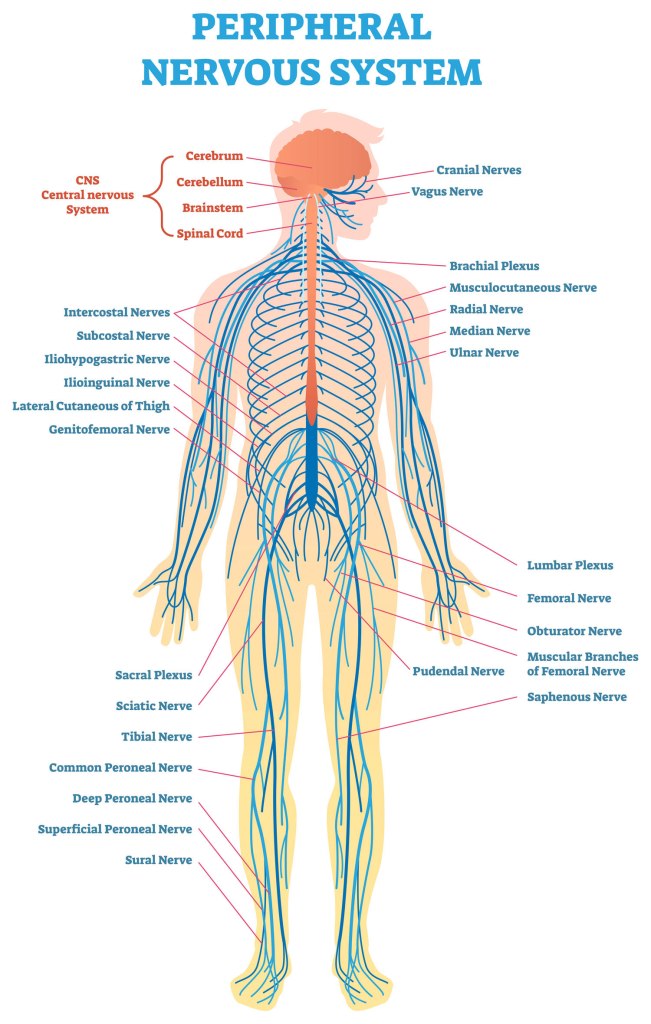
Central Nervous System (CNS): One of two parts of the nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is the body’s processing center and controls awareness, movement, speech, and thinking. The CNS is also the control center for our body’s five senses of sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste. This is the part of the nervous system affected by MS.
CIS: see Clinically Isolated Syndrome
Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS): The first episode of neurological symptoms caused by inflammation or demyelination in the central nervous system. CIS may or may not develop into MS. In CIS, the person experiences one incident that lasts at least 24 hours. In MS, the person has multiple incidents of symptoms.
CNS: see Central Nervous System
Contrast: see Gadolinium
Corticosteroid: A prescription steroid used to reduce nerve inflammation during an MS flare-up.
Crap Gap: A slang term used to describe the period of time between treatments when the medicine is wearing off and the person feels like “crap”.
Demyelination: Damage to the myelin sheath (protective covering) that surrounds nerve fibers leading to slow or blocked nerve impulses.
Diplopia: Double vision.
Disease Modifying Drug (DMD): MS treatments that interact with the immune system to calm the attack on the central nervous system. DMDs are not meant to cure the disease, but to slow it down. Interchangeable with disease-modifying therapy (DMT)
Disease-Modifying Therapy(DMT): MS treatments that interact with the immune system to calm the attack of the central nervous system. DMTs are not meant to cure the disease, but to slow it down. Interchangeable with disease-modifying drug. (DMD).
DMD: see also Disease Modifying Drug
DMT: see Disease Modifying Therapy.
Dysarthria: Difficulty speaking caused when the muscles that control speech become weakened or you have difficulty controlling them.
Dysesthesia: A burning, aching, or pins and needles pain typically in the legs and feet.
Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing.
Exacerbation: An appearance of new symptoms, or the return of old symptoms, for a period of twenty-four hours or more with a period of thirty days or more since the last relapse. This has to be in the absence of infection or an increase in core body temperature. Interchangeable with relapse.
Gadolinium: A contrast agent injected into a vein, via an IV, during an MRI scan. Contrast is used to show if there are any areas of active inflammation and if the disease is currently progressing.
HFAD: see Hip-Flexion Assist Device
Hip-Flexion Assist Device (HFAD): A device designed to improve gait. The HFAD consists of a waistband with tension bands that connect to the wearer’s shoe to assist in raising the foot from the ground and flexing the person’s hip. The HFAD is used in cases of weak hip flexors commonly seen in MS.
Hyperreflexia: Overresponsive body reflexes indicative of spinal cord damage.
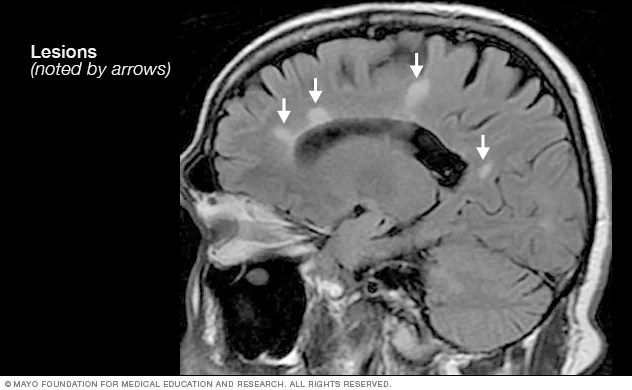
Lesion: An area of damage or scarring in the central nervous system caused by MS. Interchangeable with sclerosis or scarring.
Lhermitte’s Sign: A transient sensation of an electric shock down the spine and legs when the neck is flexed forward.
LP: see Lumbar Puncture. Interchangeable with spinal tap.
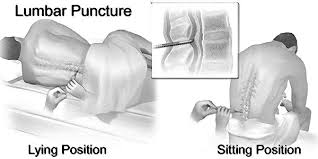
Lumbar Puncture (LP): A needle is inserted between two lumbar (lower back) vertebrae and used to withdraw spinal fluid. Analysis of the spinal fluid can determine a diagnosis of MS.
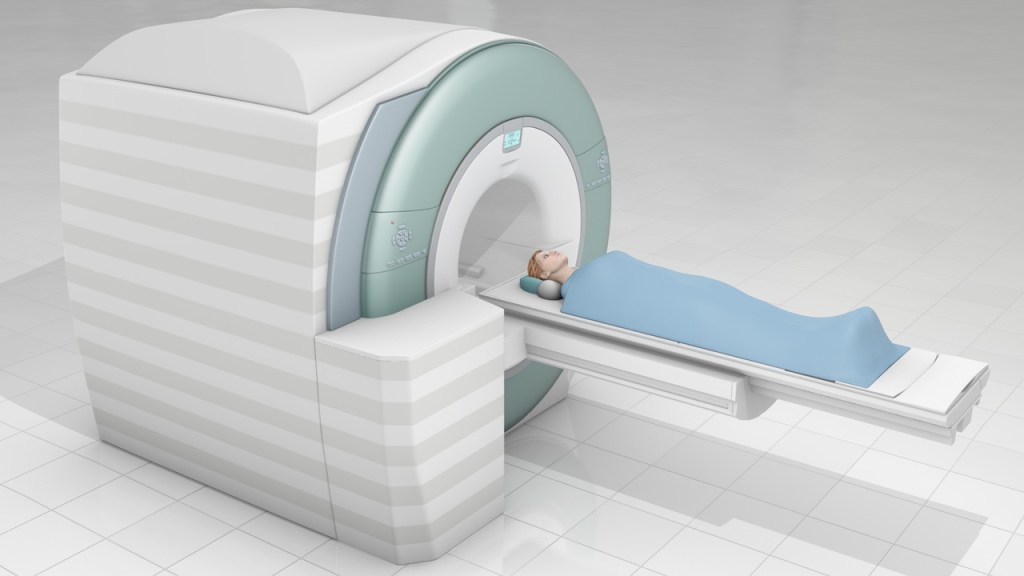
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): A medical imaging technique used in radiology to create detailed images of organs and tissue. MRI uses a strong magnetic field and computer-generated radio waves. There is no radiation exposure to the patient. MRI can show demyelination of the central nervous system and is a powerful tool for diagnosing and monitoring MS.
MRI: see Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MS: see Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): An autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the central nervous system.
Myelin: An insulating sheath that forms around nerves to allow electric impulses (messages) to transmit along the nerve cells. If damaged, messages between the brain and parts of the body may be slowed or stopped completely.
Neuron: A nerve cell. Neurons are information messengers. They use electric impulses to transmit messages between the brain and the rest of the nervous system.
Nervous System: Consists of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The nervous system is the control center of the body.
Oligoclonal Band: An immunoglobulin protein. The presence of oligoclonal bands in spinal fluid indicates inflammation in the central nervous system which may point to an MS diagnosis.
Optic Neuritis: An inflammation of the optic nerve. Common symptoms include pain with eye movement and loss of vision in the affected eye.
Peripheral Nervous System(PNS): All of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is not affected by MS.
PIRA: Progression Independent of Relapse Activity
PNS: see Peripheral Nervous System
PPMS: see Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (PPMS): A type of multiple sclerosis where symptoms gradually worsen without any associated relapses or remission.
Progression Independent of Relapse Activity (PIRA): The progression of multiple sclerosis symptoms without an associated relapse.
Pseudo-exacerbation: When symptoms appear and then go away within a twenty-four-hour period. A pseudo-relapse is temporary and usually triggered by a change in body temperature or infection. Interchangeable with pseudo-relapse
Pseudo-Relapse: When symptoms appear and then go away within a twenty-four-hour period. A pseudo-relapse is temporary and usually triggered by a change in body temperature or infection. Interchangeable with pseudo-exacerbation.
RAW: see Relapse Associated Worsening
Relapse: An appearance of new symptoms, or the return of old symptoms, for a period of twenty-four hours or more with a period of thirty days or more since the last relapse. This has to be in the absence of infection or an increase in core body temperature. Interchangeable with exacerbation.
Relapse Associated Worsening (RAW): The worsening of multiple sclerosis symptoms associated with a relapse of the disease.
Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis {(RRMS): A type of MS where symptoms worsen (relapse) and then get better (remit). RRMS is the most common form of the disease.
Remission: A phase of recovery between flare-ups when a person may experience partial or complete recovery from symptoms.
RRMS: see Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis
Sclerosis: An area of damage or scarring in the central nervous system caused by MS. Interchangeable with lesion or scarring.
Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (SPMS): The stage of the disease after relapsing-remitting MS. A person will continue to have relapses and remission, but progression starts occurring at a more steady rate.
Spasticity: A condition that occurs when there is increased stiffness of a muscle. In MS, it is usually caused by damage to the nerve pathways that control muscle movement. Spasticity can impact movement and/or speech. It can also be painful.
Spinal Tap: see Lumbar Puncture
SPMS: see Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
T-Cell: a type of white blood cell in the immune system that helps protect the body from infection. T-cells are responsible for stimulating B-cells to produce antibodies. Both are thought to play a part in MS.
Trigeminal Neuralgia: A form of neuropathic pain that affects the trigeminal nerve causing painful sensations to one side of the face. It can be brought on by light touch or movement.